Introduction
The Bitcoin Ordinals protocol has been surging, with inscriptions surpassing 58 million in January 2024. Read on to find out how this new protocol is making it possible to mint non-fungible tokens (NFTs) directly onto the Bitcoin blockchain.
Key Takeaways:
- Bitcoin NFTs have seen a considerable surge in popularity and traction since the launch of the Ordinals protocol in January 2023.
- The Ordinals protocol has made it possible to mint NFTs directly onto the Bitcoin blockchain.
- The goal of Ordinals to give each satoshi individual identities, allowing them to be tracked, transferred, and imbued with individual meanings through inscriptions.
- This allows one satoshi to be different from another, hence becoming non-fungible.
- The main advantage of Ordinals NFTs, as compared to the NFTs on other blockchains, is that Ordinals NFTs exist directly on the Bitcoin blockchain.
Why Do We Need Ordinals? A Short History of NFTs on Bitcoin
Traditionally, it is more difficult to mint NFTs on Bitcoin compared to other blockchains like Ethereum. This is due to the limited smart contract functionality on Bitcoin, as well as the lack of a token standard for NFTs, such as the ERC-721 token standard on Ethereum.
The history of NFTs on Bitcoin actually dates as far back as 2012, when the Colored Coins protocol was launched. Colored Coins were bitcoins with a mark that distinguishes them from standard bitcoins. They are considered the initial step towards NFTs built on top of the Bitcoin network.
Bitcoin NFTs have recently experienced renewed interest, with a considerable surge in popularity and traction since the launch of the Ordinals protocol in January 2023, which makes it possible to mint NFTs directly onto the Bitcoin blockchain.
What Is the Bitcoin Ordinals Protocol?
Due to their novelty, Bitcoin Ordinals NFTs involve many technical terms. here is a brief explanation of the terms used to understand how the Ordinals protocol works:
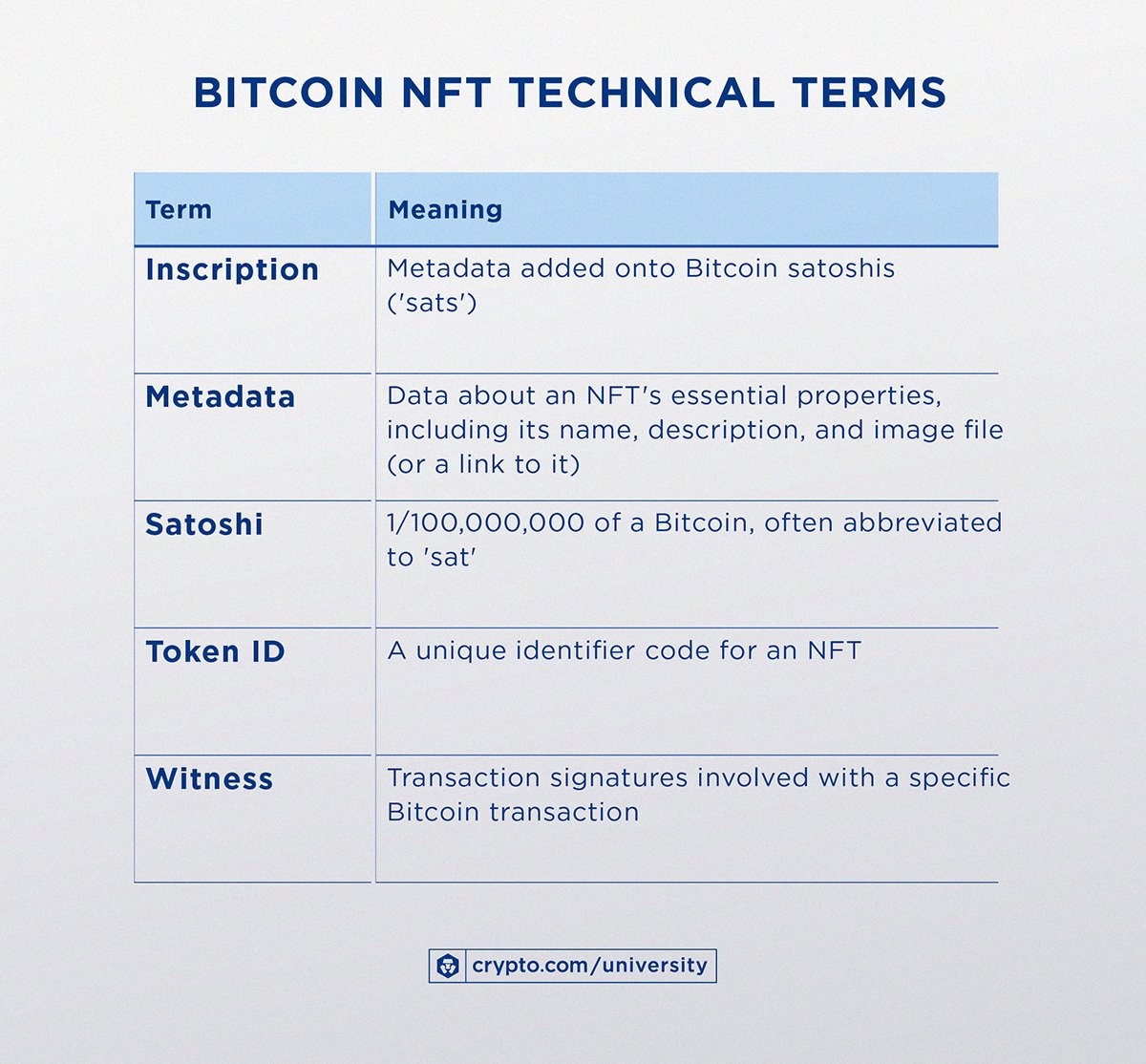
Bitcoin Ordinals NFTs are based on the Ordinal theory through the Ordinals protocol, which was developed by Casey Rodarmor. The aim of Ordinal theory is to give each satoshi (the smallest denomination of Bitcoin) individual identities, allowing them to be tracked, transferred, and imbued with unique meanings through inscriptions.
This allows one satoshi to be different from another, hence becoming non-fungible.
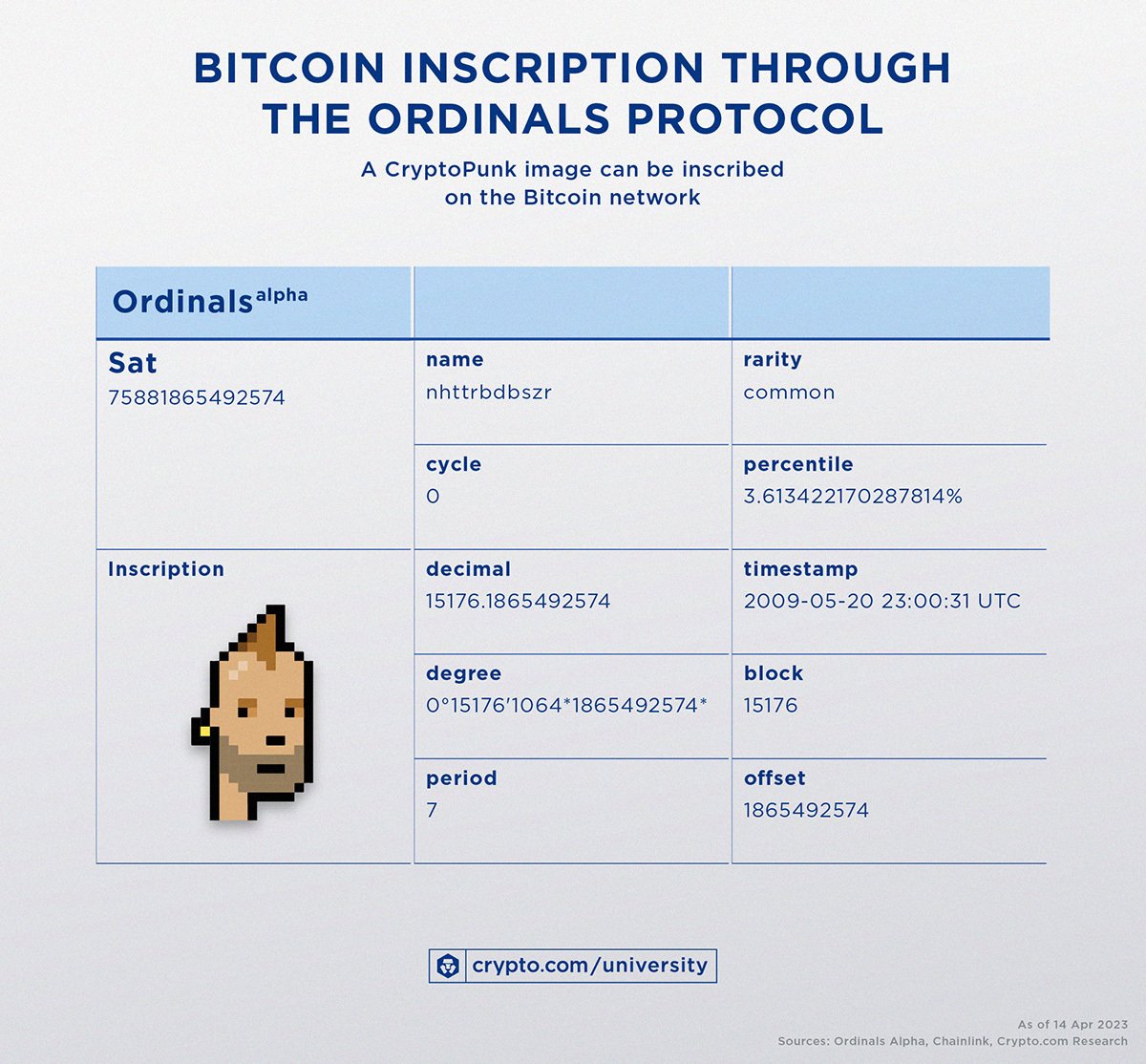
The key ideas of Ordinal theory and the Ordinals protocol include:
- The Ordinals protocol assigns each satoshi a sequential number. To be precise, each satoshi is numbered in the order mined (i.e., the first Ordinal is the first satoshi ever minted).
- Subsequently, each satoshi can be inscribed with data, such as pictures, text, or videos, through a Bitcoin transaction. Inscriptions can be up to 4 MB in size.
- After the transaction is mined, the inscribed data is permanently part of the Bitcoin blockchain. In addition, it is viewable through Ordinals-enabled Bitcoin wallets and online Ordinals viewers. For instance, the CryptoPunk image in the example above can be viewed on the Ordinals website.
- In summary, the token ID of each satoshi is its sequential number, whereas the metadata of an Ordinals NFT is its inscription held within the witness data of a transaction.
The main advantage of Ordinals NFTs, as compared to NFTs on other blockchains, is that the entire metadata is contained on the Bitcoin blockchain. In other words, Ordinals NFTs exist directly on the Bitcoin blockchain and not on a separate layer from Bitcoin. This is viewed by many as having an increased level of immutability.
In contrast, for many NFT collections on other blockchains, the actual image file of the art is typically stored off-chain, and the metadata just includes a link to the image file. This implies that the artwork can potentially be altered by third parties if it is not stored on the blockchain.
Other Developments in Bitcoin NFTs
The Bitcoin Stamps (Secure Tradeable Art Maintained Securely) protocol is a recent development that proposes a different method of embedding image data onto Bitcoin, as compared to the Ordinals protocol.
Bitcoin Stamps NFTs are similar to ERC-1155 semi-fungible tokens or digital collectibles, but they are stored on Bitcoin’s unspent transaction outputs (UTXOs) rather than in the witness data like with Ordinals. UTXOs are records of unspent bitcoins that result from transactions between two addresses. The way the Bitcoin Stamps protocol stores metadata makes it impossible to prune (i.e., remove data) from a full node and helps in immutably preserving the data.
Bitcoin Ordinals vs Bitcoin Stamps
| Ordinals | Stamps | |
|---|---|---|
| Pros | Stores image data within prunable transaction witness data, thus a lower cost to mint NFTs compared to Stamps (which stores data across many different UTXOs). | Image data is not possible to prune from a full node, as it is stored across many different UTXOs. This helps in immutab |
| Cons | NFT data potentially can be pruned by individual node runners, which limits the immutability and decentralisation benefits of the NFTs. | Higher costs due to storing data across all Bitcoin nodes. The Stamps protocol creator suggests limiting the image resolution and size to lightweight 24×24 pixel, 8-colour-depth PNG or GIF files. |
| Pros | |
| Ordinals | Stores image data within prunable transaction witness data, thus a lower cost to mint NFTs compared to Stamps (which stores data across many different UTXOs). |
| Stamps | Image data is not possible to prune from a full node, as it is stored across many different UTXOs. This helps in immutab |
| Cons | |
| Ordinals | NFT data potentially can be pruned by individual node runners, which limits the immutability and decentralisation benefits of the NFTs. |
| Stamps | Higher costs due to storing data across all Bitcoin nodes. The Stamps protocol creator suggests limiting the image resolution and size to lightweight 24×24 pixel, 8-colour-depth PNG or GIF files. |
Besides protocols like Bitcoin Ordinals and Bitcoin Stamps that directly build on the base layer, Bitcoin NFTs can also be created on Bitcoin Layer-2s that allow for smart contracts to be executed and transactions to be settled, making the creation and exchange of Bitcoin NFTs more cost-effective, sustainable, and scalable. Examples of Bitcoin Layer-2s that support smart contracts and NFTs include Stacks, Rootstock, and Liquid Network.
Read more about Bitcoin Layer-2s and other developments of the Bitcoin ecosystem in Bitcoin’s Expanding Ecosystem: Layer-2, DeFi, NFT.
Popular Bitcoin Ordinals
Some popular Bitcoin Ordinals NFT projects are based on their Ethereum counterparts. For example, Ordinal Punks and Bitcoin Punks are based on CryptoPunks. But as Ordinals are making a name for themselves, native projects are gaining popularity, like BitcoinShrooms.
Ordinal Punks
The Ordinal Punks collection consists of 100 unique PFPs (profile pictures) that are created entirely on-chain on the Bitcoin blockchain during the first 650 inscriptions. Ordinal Punks utilise an open-source algorithm to generate the PFP, which has a size of 192×192 pixels.
TwelveFold
Top NFT brands are also participating in Ordinals. Yuga Labs, the company behind top Ethereum-based NFT collection Bored Ape Yacht Club, recently launched its first Bitcoin Ordinals NFT collection called TwelveFold. It consists of 300 unique generative art pieces inscribed onto satoshis on the Bitcoin blockchain.
BitcoinShrooms
In December 2023, Sotheby’s New York launched an online auction featuring BitcoinShrooms from the Bitcoin Ordinals collection by Shroomtoshi. The project fuses Bitcoin’s history, culture, and core technicalities into individual Shroom Ordinals that are unique, pixelated, hand-crafted pieces of art that represent milestones in Bitcoin’s history.
Domain Name Projects
Other notable Bitcoin-based NFT projects include Bitcoin domain names. These aim to provide similar functionalities to Ethereum domain names, such as Ethereum Name Service (ENS). Stacks is a Bitcoin Layer-2 solution that provides a .BTC domain name as a decentralised web identity and human-readable wallet address.
Ordinals and the BRC-20 Token Standard
The BRC-20 token standard is an experimental fungible token standard for the Bitcoin blockchain. It was created by an anonymous on-chain analyst named ’domo’ in March 2023. Inspired by Ethereum’s ERC-20, BRC-20 tokens enable developers to create and transfer fungible tokens using the Ordinals protocol. However, unlike ERC-20, BRC-20 tokens do not make use of smart contracts.
The BRC-20 token standard utilises Ordinals inscriptions of JSON data to deploy, mint, and transfer tokens. Currently, over 34,000 BRC-20 tokens have been minted — like ORDI, the first BRC-20 token.
Read more in What Is the BRC-20 Token Standard for Bitcoin?
Conclusion
Bitcoin NFTs have seen a considerable surge in popularity and traction since the launch of the Ordinals protocol in January 2023, which has made it possible to mint NFTs directly onto the Bitcoin blockchain.
Bitcoin Ordinals NFTs are based on the Ordinal theory through the Ordinals protocol, which aims to give each satoshi unique identities, allowing them to be tracked, transferred, and imbued with individual meanings through inscriptions. This allows one satoshi to be different from another, hence becoming non-fungible. Other notable developments in Bitcoin NFTs are the Stamps protocol and Bitcoin domain names.
For further reading, check out our Bitcoin hub for everything BTC.
Due Diligence and Do Your Own Research
All examples listed in this article are for informational purposes only. You should not construe any such information or other material as legal, tax, investment, financial, or other advice. Nothing contained herein shall constitute a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, or offer by Crypto.com to invest, buy, or sell any coins, tokens, or other crypto assets. Returns on the buying and selling of crypto assets may be subject to tax, including capital gains tax, in your jurisdiction.
Past performance is not a guarantee or predictor of future performance. The value of crypto assets can increase or decrease, and you could lose all or a substantial amount of your purchase price. When assessing a crypto asset, it’s essential for you to do your research and due diligence to make the best possible judgement, as any purchases shall be your sole responsibility.